微调deepseek-R1的喂饭级入门教程
之前我们已经介绍如何部署deepseek-R1,今天这篇我们更进一步,来微调一个自己的deepseek-R1模型。 我们以一个中文medical cot数据集为例,来进行微调。 这个medical cot数据集,是一个medical领域的数据集,包含了很多medical相关的问题和答案。 我们可以使用这个数据集来微调deepseek-R1,让deepseek-R1能够更好地回答medical相关的问题。 下边的每行代码,每个参数都有注释,这也是我自己学习的过程,代码逻辑很简单,大家可以跟着我的思路,一步一步来。
先声明一下我的环境
相同的代码,在不同环境下,运行的结果可能不一样,所以,我这里声明一下我的环境,大家最好和我的环境一致,保证微调可以顺利进行。 因为我使用的是kaggle的资源,在settings选项卡中,Environment Preferences选择的是Always use the same environment, 我的运行环境如下: Platform: Linux python :3.11.13 wandb version 0.20.1 Unsloth 2025.7.3 Transformers: 4.52.4 GPU: Tesla T4 * 2 Torch: 2.6.0+cu124. CUDA: 7.5. CUDA Toolkit: 12.4. Triton: 3.2.0
这个环境会因为是用的最新的环境配置,所以可能会不断变化,上边最重要的是python版本,使用3.11以上的,其它的版本,可以用最新的。
1、在kaggle中配置好项目环境
在菜单栏的Settings选项卡中,有三个选项: a、Trun on internet : 代码执行过程中,需要网络下载相关的库。 b、Accelerator: 选择需要的GPU资源。我们选择T4 * 2 c、Environment Preferences: 代码的运行环境,我们选择 Always use the latest environment,
在菜单栏的Add-ons选项卡中,有Secrets选项:是用来设置环境变量的。我设置了调用huggingface和wandb的2个密钥,
因为后边微调会用到。
2、查看自己环境
|
|
如果输出是3.11.13 (main, Jun 4 2025, 08:57:29) [GCC 11.4.0],和我的环境一致
3、安装微调工具unsloth
安装涉及到的库,最重要的是unsloth相关的库,unsloth是一个微调工具,我们使用它来微调deepseek-R1。 简单介绍一下unsloth,我们引用unsloth的官方介绍:Finetune Gemma 3n, Qwen3, Llama 4, Phi-4 & Mistral 2x faster with 80% less VRAM! 翻译成中文就是:使用unsloth,我们可以快速地微调Gemma 3n, Qwen3, Llama 4, Phi-4 & Mistral 2x,并且使用更少的VRAM。 unsloth的官方介绍:https://unsloth.ai/ 其它一些库,是umsloth的依赖库,如果运行时,提示还缺少某个依赖,根据自己环境安装就可以。
|
|
4、安装涉及的其它库
|
|
5、登录wandb和huggingface
|
|
6、加载DeepSeek R1模型和分词器
|
|
7、定义一个提示词,用于测试一下没有微调前模型的效果。
|
|
8、运行模型推理,查看模型推理效果
|
|
大模型回答内容:
She underwent a gynecological exam and a Q-tip test. I’m not entirely sure about the specifics of the Q-tip test, but I think it’s used to assess urethral function. Maybe it helps determine if the urethral sphincter is functioning properly. If the Q-tip test is positive, it might mean that the sphincter has some activity, which could contribute to her symptoms.
Now, about cystometry. From what I remember, cystometry, or urodynamic testing, involves filling the bladder and measuring how it reacts under different conditions. They usually fill the bladder with a fluid, and then they check how much volume is left after the patient can’t hold it anymore (residual volume). Then they might stimulate the bladder (like by tickling the nerve) to see if there are detrusor contractions, which are involuntary contractions of the detrusor muscle.
Given her history, she’s likely experiencing stress urinary incontinence because she loses urine on coughing or sneezing, which are activities that put pressure on the bladder. But since she doesn’t leak at night, it’s probably not a case of genuine urinary incontinence, which can happen at any time, including sleep.
So, in the cystometry, the residual volume would probably be low because she can hold her urine until she needs to release it, especially when the activity that causes the leak isn’t happening. But when she does lose it, the detrusor contractions might be increased because the bladder is trying to empty involuntarily when the pressure is applied, like from coughing.
Wait, but I’m a bit confused. If she doesn’t leak at night, maybe her bladder capacity is normal, and the detrusor contractions are normal. But when she does activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, the contractions become stronger, leading to leakage. So in the cystometry, when they simulate those conditions, the detrusor contractions would show increased activity.
But I’m not entirely sure. Maybe I should think about the types of incontinence. Stress incontinence is due to weak pelvic floor muscles or urethral sphincter deficiency, which can be assessed with the Q-tip test. If the Q-tip test is positive, it suggests that the sphincter is not functioning well, which would mean that when pressure is applied, the sphincter can’t prevent the urine from leaking.
So in the cystometry, the detrusor contractions might be normal, but the compliance of the bladder might be normal as well. The issue is more about the sphincter’s ability to prevent leakage. So maybe the detrusor contractions are normal, but the residual volume is low because she can hold her urine until it’s no longer possible.
Wait, but the question is specifically about residual volume and detrusor contractions. So residual volume is the amount of urine left in the bladder after she can’t hold it. In stress incontinence, the residual volume is usually normal because the problem is not with emptying the bladder completely, but with the sphincter’s ability to prevent leakage when under pressure.
So, the residual volume would be within normal limits, and the detrusor contractions would be normal as well. The issue is more in the sphincter function, which isn’t measured directly in cystometry but in tests like the Q-tip.
Hmm, I’m getting a bit tangled here. Let me try to organize my thoughts:
- Patient has stress urinary incontinence symptoms (leak on cough/sneeze) but no leakage
- at night.
- Underwent gynecological exam and Q-tip test.
- Q-tip test: Positive if the urethral sphincter doesn’t function properly.
- Cystometry: Measures residual volume and detrusor contractions.
- In stress incontinence, the detrusor contractions are usually normal, and the issue is
- sphincter deficiency.
- So, in cystometry, residual volume is normal, and detrusor contractions are normal.
But wait, sometimes in stress incontinence, the detrusor contractions might be slightly increased when the patient is under pressure, but I’m not sure. Maybe it’s more about the sphincter’s resistance.
Alternatively, maybe the detrusor contractions are normal, and the issue is that the sphincter can’t prevent the leakage, so the residual volume is normal.
I think the key point is that in stress incontinence, the main problem is the sphincter, not the detrusor muscle. So, the cystometry would show normal residual volume and normal detrusor contractions. The sphincter function would be impaired, which is why the Q-tip test would be positive.
So, the answer is that cystometry would show normal residual volume and normal detrusor contractions.
Based on the analysis of the patient’s history and the Q-tip test results, the cystometry would reveal normal residual volume and normal detrusor contractions. The primary issue appears to be related to the urethral sphincter’s inability to prevent leakage, indicating stress urinary incontinence. Therefore, the findings of the cystometry would not show increased detrusor contractions but would instead highlight a sphincter deficiency.
有兴趣的朋友可以把这段话翻译成中文,可以看到这个回答比较的啰嗦,而且AI味道比较重。现在我们微调一个我们使用的 推理模型:Fine-tune-DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B。微调一个我们自己的私人医生模型。
9.修改一下微调的提示词,和原来提示词的区别是,加了一个点位符{},这个是为了适应我们的微调数据集。
train_prompt_style = “““Below is an instruction that describes a task, paired with an input that provides further context. Write a response that appropriately completes the request. Before answering, think carefully about the question and create a step-by-step chain of thoughts to ensure a logical and accurate response.
Instruction:
You are a medical expert with advanced knowledge in clinical reasoning, diagnostics, and treatment planning. Please answer the following medical question.
Question:
{}
Response:
10.下载新的微调数据集
|
|
打印数据集中一条数据看看:
|
|
{ ‘Question’: ‘A 33-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 15 minutes after being stabbed in the chest with … ‘Complex_CoT’: “Okay, let’s figure out what’s going on here. A woman comes in with a stab wound from a screwdriver. It… ‘Response’: ‘In this scenario, the most likely anatomical structure to be injured is the lower lobe of the left lung…. } 一条完整的微调数据,包含3个字段:Question, Complex_CoT, Response。其中Question是患者的问题,Complex_CoT是患者的问题背景,Response是医生的回答。
11、格式化数据集中的数据,适应我们新定义的微调提示词。
|
|
简单介绍一下train_prompt_style.format(input, cot, output):
将 input, cot, output 的值填充到一个预定义的 文本模板(train_prompt_style)中,
示例模板可能类似:
这个模板包含三个占位符:{0}, {1}, {2},它们会被分别替换为 input, cot, output 的值。
这就可以让我们理解新的微调提示词中多出一个占位符的原因。
12、生成新的微调数据集
|
|
新的数据集格式如下 Below is an instruction that describes a task, paired with an input that provides further context. Write a response that appropriately completes the request. Before answering, think carefully about the question and create a step-by-step chain of thoughts to ensure a logical
Instruction:
You are a medical expert with advanced knowledge in clinical reasoning, diagnostics, and treatment planning. Please answer the following medical question.
Question:\nGiven the symptoms of sudden weakness in the left arm and leg, recent long-distance travel, and…
Response:\n\nOkay, let’s see what’s going on here.
\nThe specific cardiac abnormality most likely to be found in this scenario is a patent foramen ovale (PFO).
可以看到response中包括2个占位符
13、定义微调技术参数
这里使用的微调技术是LoRA, 简称Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models (LoRA)。微调的技术方案有很多种,比如LoRA、PEFT、QLoRA、Adapter、 Prefix Tuning等。但是,经过工程实践证明,LoRA是目前最有效的微调技术。 下边涉及的这些参数,大家明白是什么意思就行,没必要去纠结为什么那这些参数,而不是其它参数。大模型的参数太多,微调的参数也太多,想全部搞清楚,对于新手来说, 不可能,也完全没必要。学习新知识,先疏理核心知识点最重要。
|
|
14、初始化训练器
|
|
关键参数说明: 梯度累积: 小批量多次计算梯度后统一更新,突破GPU显存限制 学习率预热: 训练初期逐步提升学习率,避免模型参数剧烈震荡 精度加速: fp16:半精度浮点,兼容性广 ,bf16:脑浮点格式,动态范围更大(需Ampere+架构GPU) 内存优化: adamw_8bit优化器减少70%显存占用,允许更大批量训练 训练终止: max_steps=60常用于快速验证流程,生产环境需移除或增大该值
15、最激动人心的时刻,微调开始
|
|
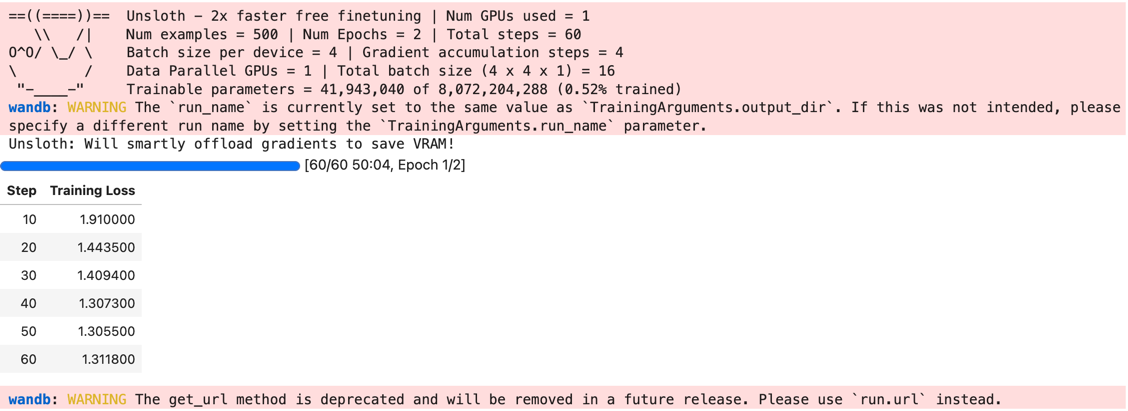
16、保存微调后的模型
|
|
17、测试微调后的模型效果
|
|
微调后的模型回答:
Now, she’s had a gynecological exam and a Q-tip test. Hmm, let’s think about what those tests usually show. The Q-tip test is a pretty standard way to figure out if there’s a urethral obstruction. If it’s positive, it means the urethra is kind of narrowed or blocked, which would explain why she’s having these episodes of leakage.
Let’s imagine the Q-tip test came back positive. That would mean there’s an obstruction in the urethra, probably causing some kind of pressure buildup in her bladder. This kind of situation can lead to increased bladder pressure, which might make the bladder want to contract more often than usual to release that pressure. So, if the bladder contracts more often, we’d expect the person to have more involuntary contractions.
Now, about the cystometry. Cystometry is like a bladder diary on steroids. It shows how much urine is left in the bladder at different times and how the bladder responds to filling up. If the bladder is contracting more often, you’d see more contractions in the cystometry.
But here’s the kicker: she doesn’t leak at night. This suggests that her bladder doesn’t stay full to the point where it’s leaky during sleep. So, even though she’s having a lot of contractions, she’s not accumulating enough urine to leak at night.
This makes me think about the concept of ’leakage’ versus ‘functional’ bladder capacity. She’s leaking during activities, but her bladder is still working to hold up during sleep. It’s like her bladder is managing to hold the urine well when she’s resting, even though it’s not holding up during other activities.
So, if the Q-tip test is positive and the cystometry shows more contractions, we’d expect to see a lot of contractions, but the residual volume wouldn’t be too high, and she wouldn’t leak at night because the bladder is still functional in sleep.
Yeah, that makes sense. It fits with what we know about how the bladder behaves in these situations. It’s all about balancing the bladder’s ability to hold urine versus its tendency to leak when there’s pressure. Based on the findings from the Q-tip test, which is positive, indicating urethral obstruction, and the fact that the woman does not leak at night, cystometry would most likely reveal that her bladder has increased contractions (due to the pressure buildup from the obstruction) but not a significantly high residual volume. This suggests that her bladder is functional enough to retain urine during sleep, despite the increased contractions during activities like coughing or sneezing. Therefore, cystometry would show more contractions, but the residual volume would not be excessively high. <|end▁of▁sentence|>
新的模型回答明显比之前的简洁,也没有浓浓的AI味道。
从整个微调的过程来看,并没有特别的难点,自己实践的话,环境最好和我的保持一致,不然, 可能会出现一些问题。 还有就是,如果你微调其它数据,有一份合适的微调数据集也是重要的。
- 原文作者: 三山
- 原文链接: https://blog.jinerge.com:443/aitools/deepseek/fine-tuning/deepseek_fine-tuning-4.html
- 版权声明:本作品采用 署名 - 非商业性使用 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC 4.0)进行许可,非商业转载请注明出处(作者,原文链接),商业转载请联系作者获得授权。


